Chapter 11 Forecasting I
Data for this chapter:
The
msalesandqalesdata are used from theMKT4320BGSUcourse package. Load the package and use thedata()function to load the data.
11.1 Introduction
While Base R does have some time-series forecasting capabilities, there are several packages that make working with the data and running the analysis easier. For our class, we will be mainly using the fpp3 package inside of some user-defined functions. The user-defined functions are described briefly below, and then in detail in their own sections.
11.1.1 User-Defined Functions for Forecasting I
naivefcanalyzes the data using naive forecasting methodssmoothfcanalyzes the data using smoothing forecasting methodslinregfcanalyzes the data using regression-based forecasting methodstsplotproduces a time series plot of the datafccomparecompares models from saved results after running the methods functions
11.2 tsplot User Defined Function
- Usage:
tsplot(data, tvar="", obs="", datetype=c("ym", "yq", "yw"), h= )datais the name of the dataframe with the time variable and measure variabletvaris the variable that identifies the time period (in quotes)obsis the variable that identifies the measure (in quotes)datetypecan be one of three options:"ym"if the time period is year-month"yq"if the time period is year-quarter"yw"if the time period is year-week
his an integer indicating the number of holdout/forecast periods
- Output: A time series plot
tsplot(msales, # Dataframe
"t", # Date variable
"sales", # Measure variable
"ym", # Date type
12) # Holdout periods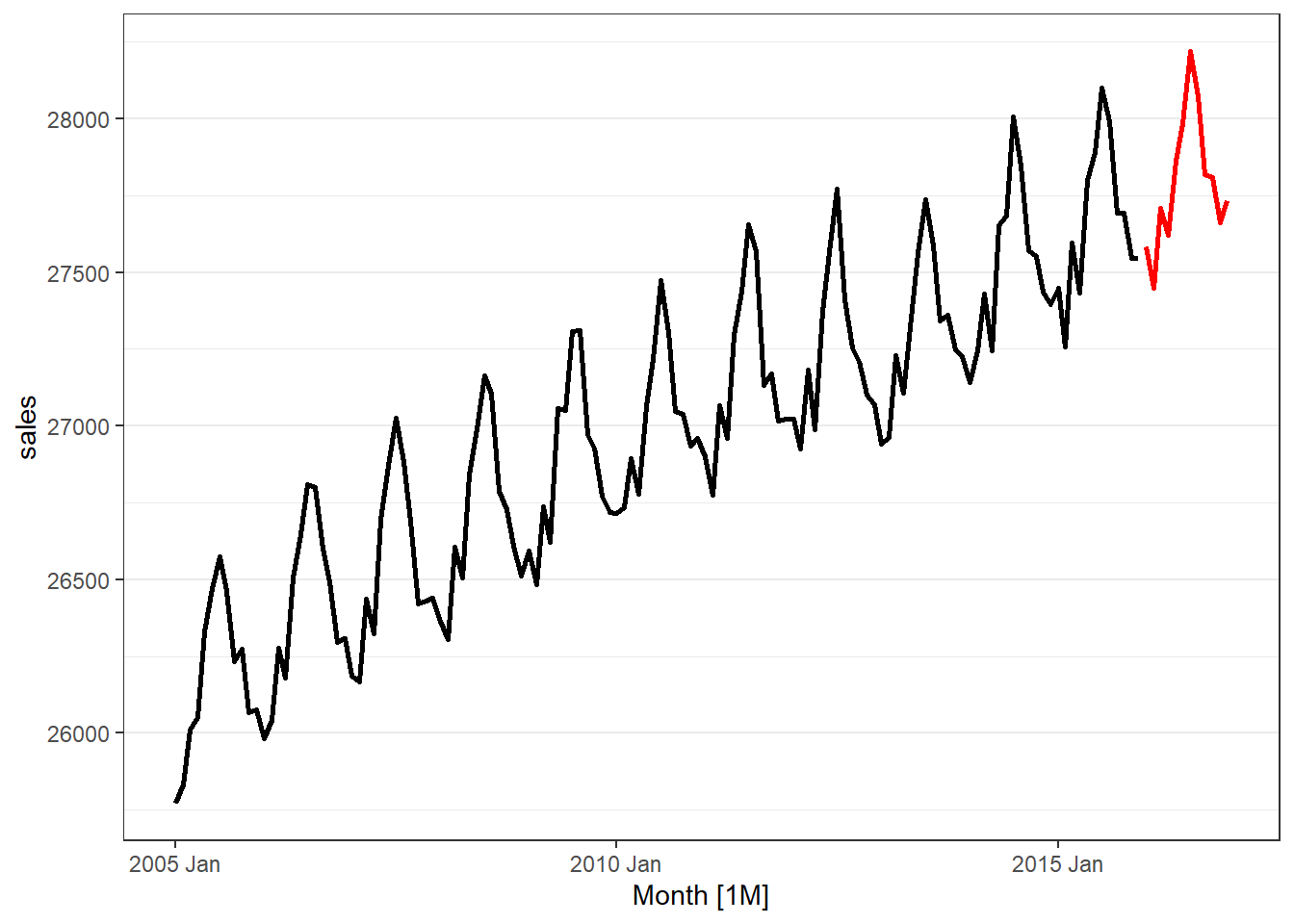
11.3 naivefc User Defined Function
- Usage:
naivefc(data, tvar="", obs="", datetype=c("ym", "yq", "yw"), h= )datais the name of the dataframe with the time variable and measure variabletvaris the variable that identifies the time period (in quotes)obsis the variable that identifies the measure (in quotes)datetypecan be one of three options:"ym"if the time period is year-month"yq"if the time period is year-quarter"yw"if the time period is year-week
his an integer indicating the number of holdout/forecast periods
- NOTE 1: The results of this function should be saved to an object. When doing so, the following objects are returned:
$plotcontains the naive methods plot$acccontains the accuracy measures$fcresplotcontains a plot of the holdout period residuals$fcresidis a dataframe of the holdout period residuals (seldom used separately)
- Note 2: The model names are:
- Naive for the naive model
- Naive.Drift for the naive model with drift
- Seas.Naive for the seasonal naive model
- Seas.Naive.Drift for the seasonal naive model with drift
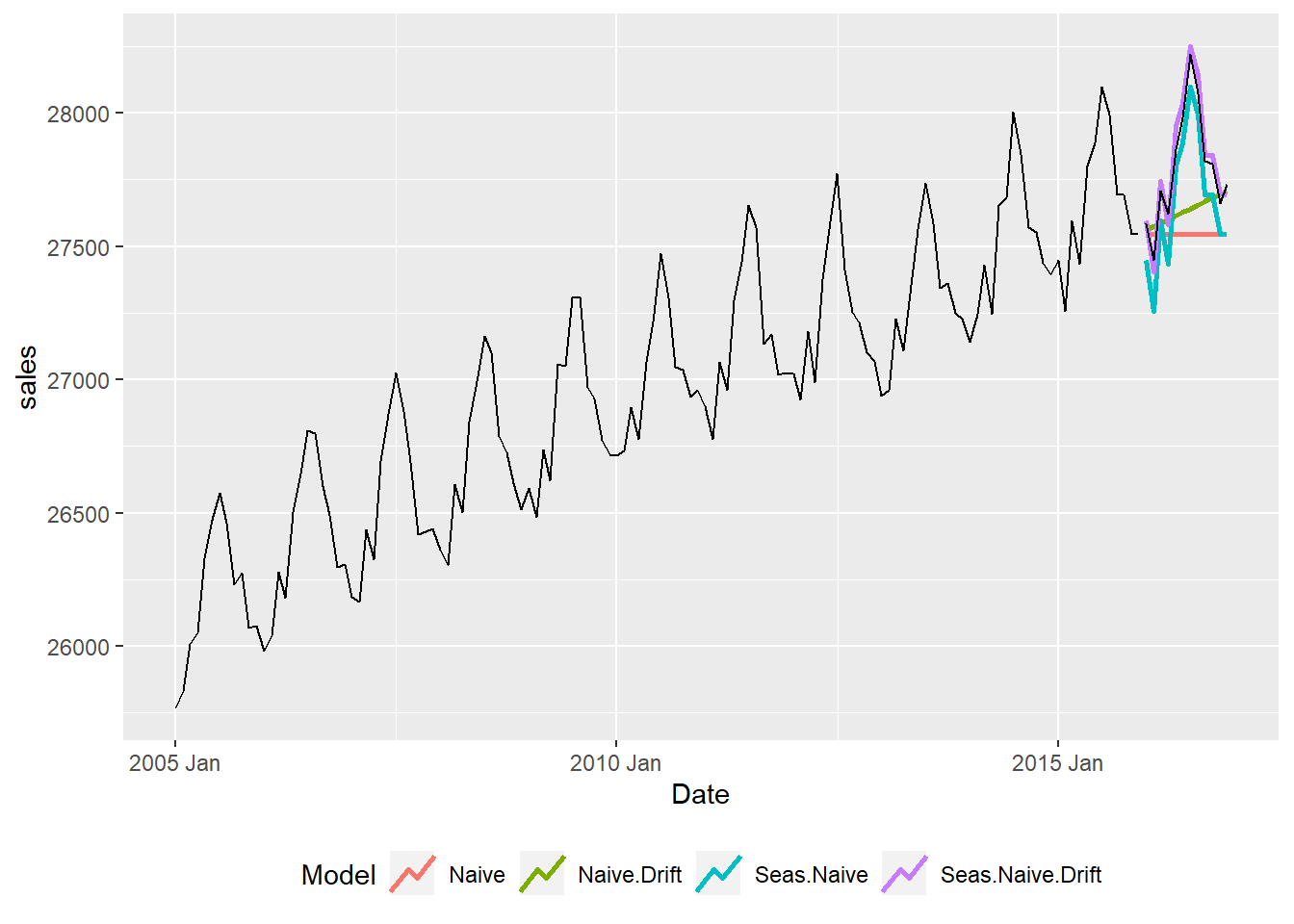
Model RMSE MAE MAPE
1 Naive 323.496 263.917 0.945
2 Naive.Drift 253.103 185.868 0.665
3 Seas.Naive 133.710 127.417 0.459
4 Seas.Naive.Drift 45.769 41.417 0.149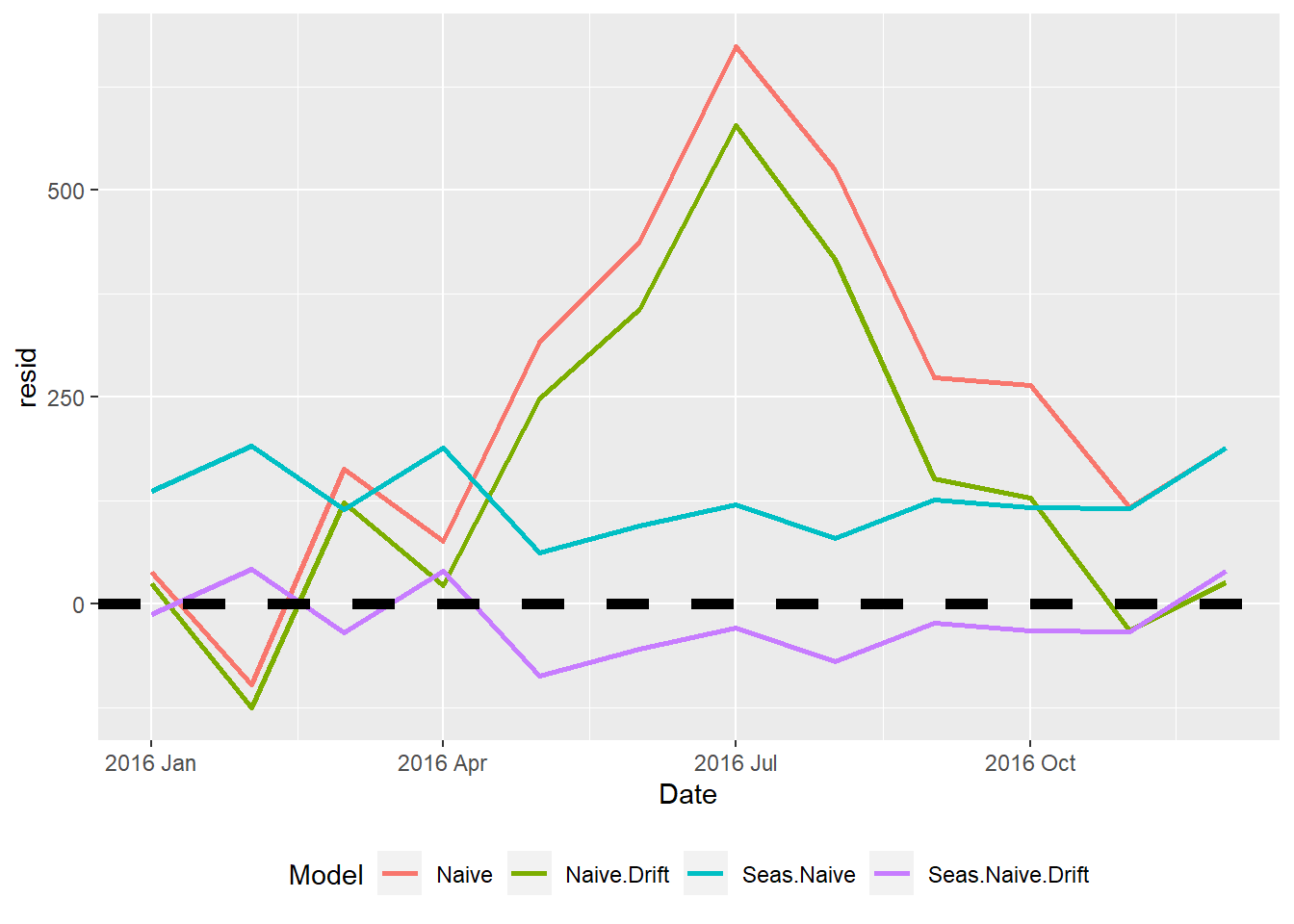
11.4 smoothfc User Defined Function
- Usage:
smoothfc(data, tvar="", obs="", datetype=c("ym", "yq", "yw"), h= )datais the name of the dataframe with the time variable and measure variabletvaris the variable that identifies the time period (in quotes)obsis the variable that identifies the measure (in quotes)datetypecan be one of three options:"ym"if the time period is year-month"yq"if the time period is year-quarter"yw"if the time period is year-week
his an integer indicating the number of holdout/forecast periods
- NOTE 1: The results of this function should be saved to an object. When doing so, the following objects are returned:
$plotcontains the smoothing methods plot$acccontains the accuracy measures$fcresplotcontains a plot of the holdout period residuals$fcresidis a dataframe of the holdout period residuals (seldom used separately)
- Note 2: The model names are:
- Mov.Ave for the moving average model
- Exp.Smooth for the exponential smoothing model
- H-W.Add for the Holt-Winters Additive model
- H-W.Mult for Hold-Winters Multiplicative model
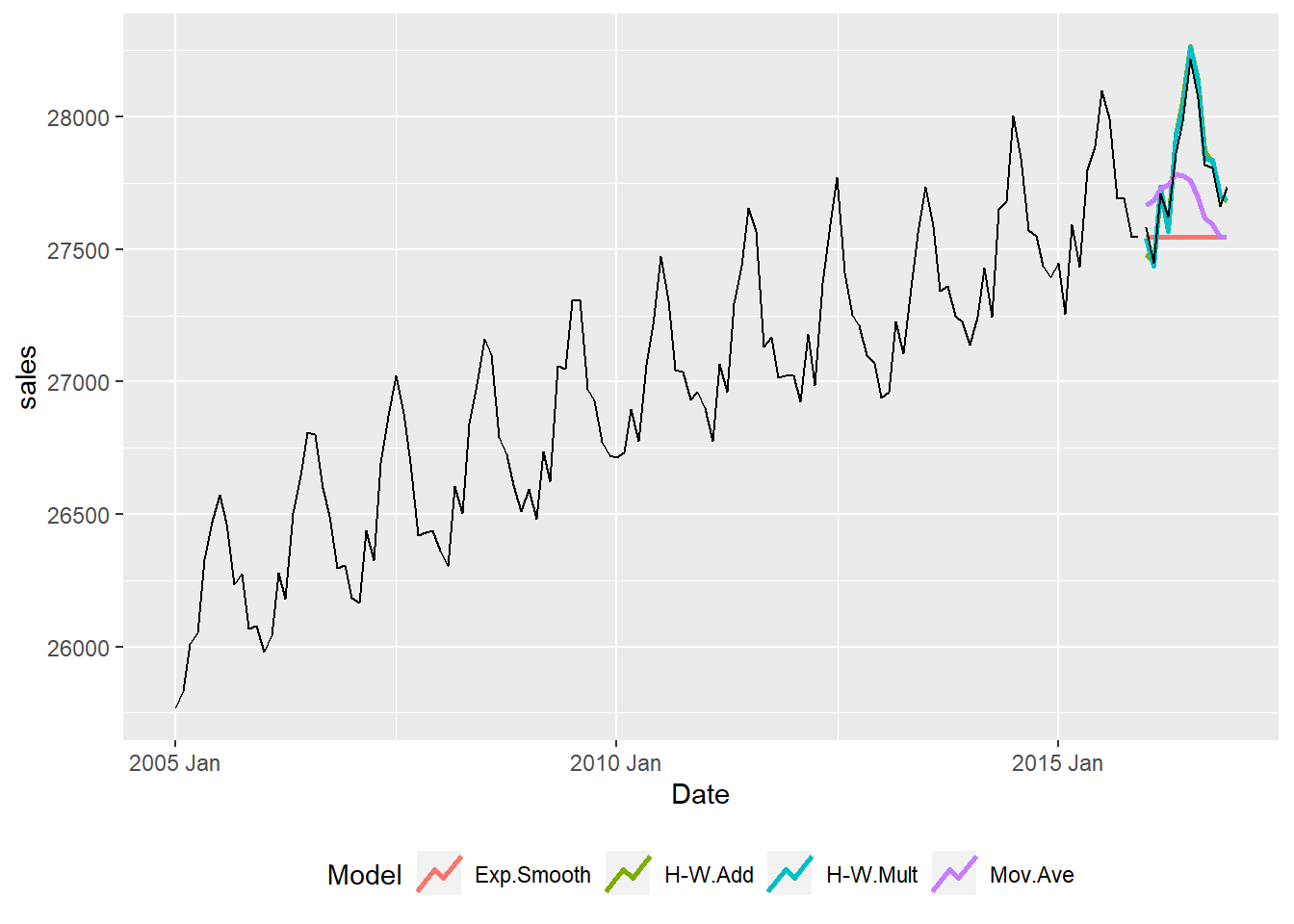
Model RMSE MAE MAPE
1 Exp.Smooth 323.495 263.915 0.945
2 H-W.Add 54.469 46.754 0.168
3 H-W.Mult 43.857 40.626 0.146
4 Mov.Ave 225.685 191.245 0.686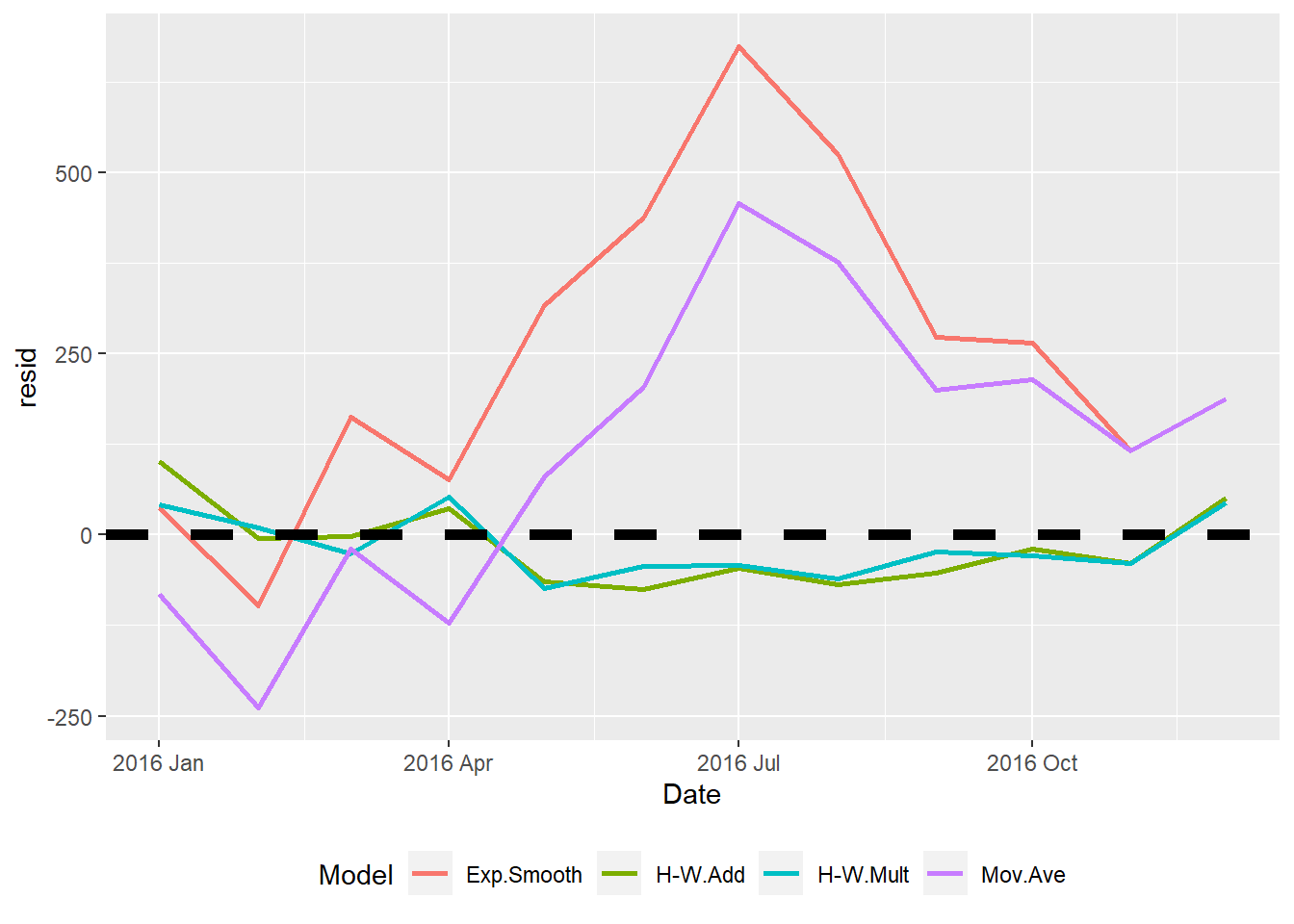
11.5 linregfc User Defined Function
- Usage:
linregfc(data, tvar="", obs="", datetype=c("ym", "yq", "yw"), h= )datais the name of the dataframe with the time variable and measure variabletvaris the variable that identifies the time period (in quotes)obsis the variable that identifies the measure (in quotes)datetypecan be one of three options:"ym"if the time period is year-month"yq"if the time period is year-quarter"yw"if the time period is year-week
his an integer indicating the number of holdout/forecast periods
- NOTE 1: The results of this function should be saved to an object. When doing so, the following objects are returned:
$plotcontains the regression methods plot$acccontains the accuracy measures$fcresplotcontains a plot of the holdout period residuals$fcresidis a dataframe of the holdout period residuals (seldom used separately)
- Note 2: The model names are:
- Lin.Reg.Trend for the linear regression with trend model
- Line.Reg.Seas.Trend for linear regression with trend and seasonality model
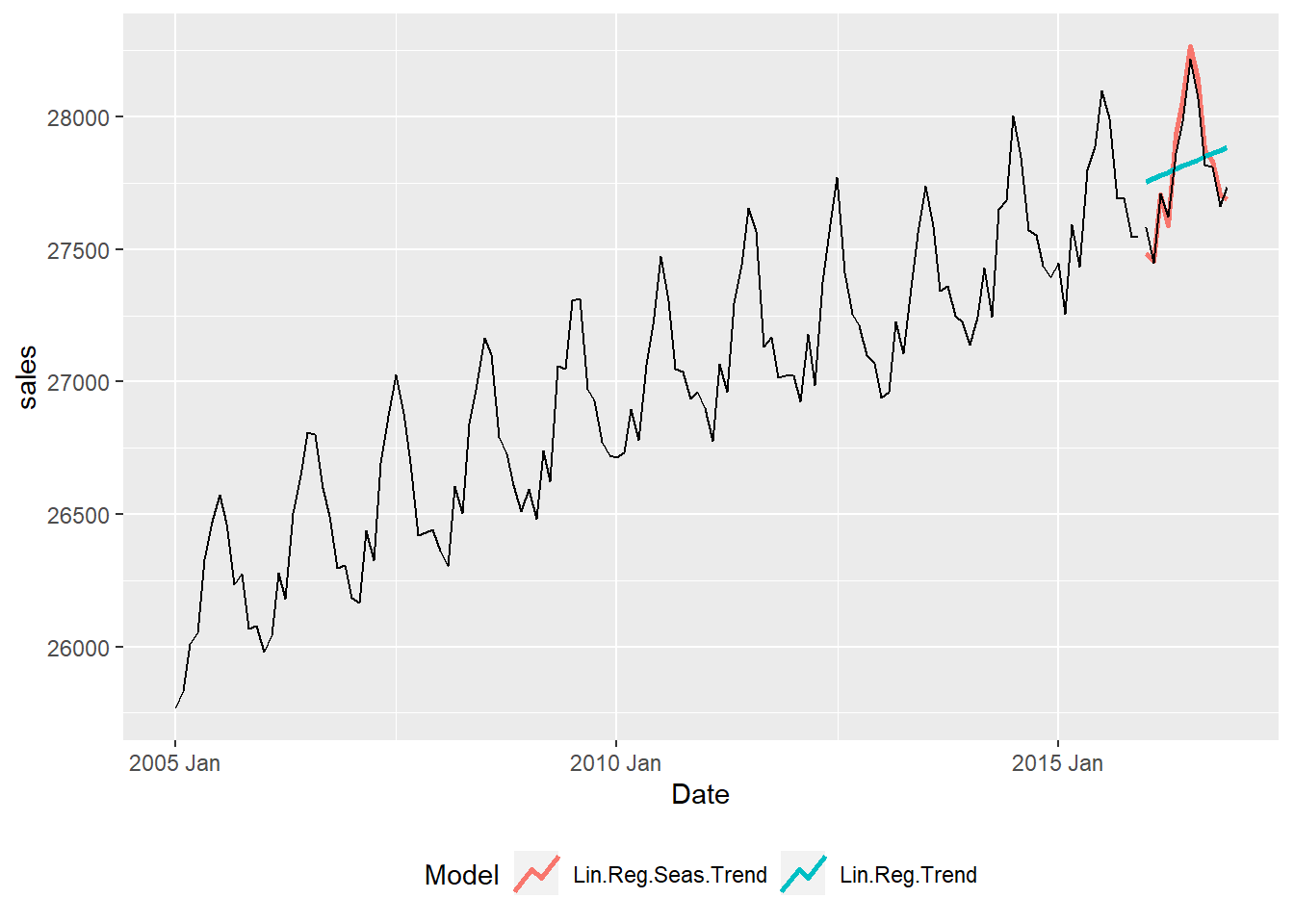
Model RMSE MAE MAPE
1 Lin.Reg.Seas.Trend 55.212 47.898 0.172
2 Lin.Reg.Trend 199.198 168.985 0.607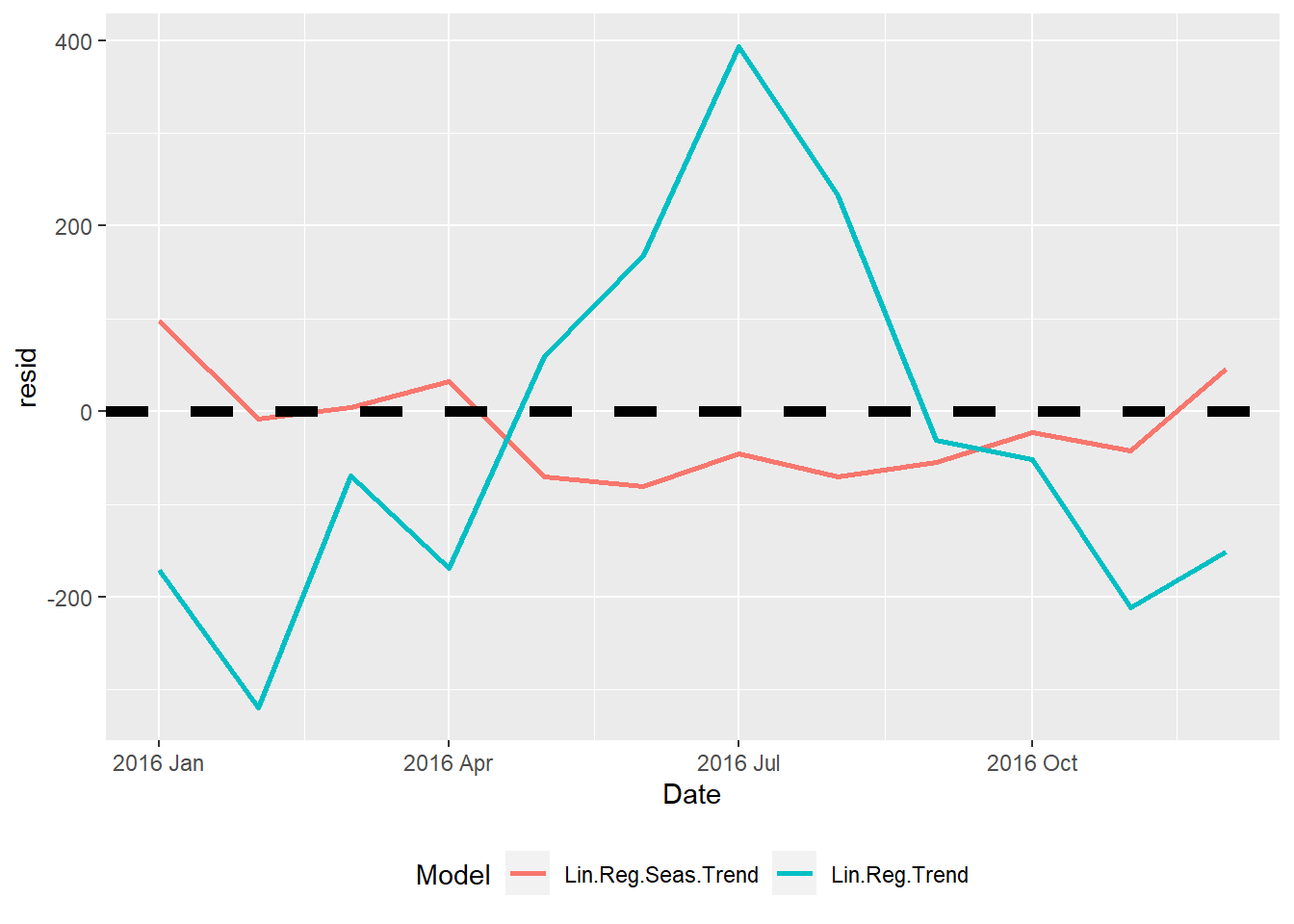
11.6 fccompare User Defined Function
- Usage:
fccompare(results, models)resultsis a list of the stored methods results; create the list with thelistfunction, such as:results <- list(naive, smooth, linreg)modelsis a vector of the models you want to compare; create the vector with thec()function, such as:models <- c("Naive", "Mov.Ave", "Lin.Reg.Trend")
- NOTE 1: The function returns two items that will be directly displayed or can be saved to an object:
$acccontains the accuracy measures$fcresplotcontains a plot of the holdout period residuals
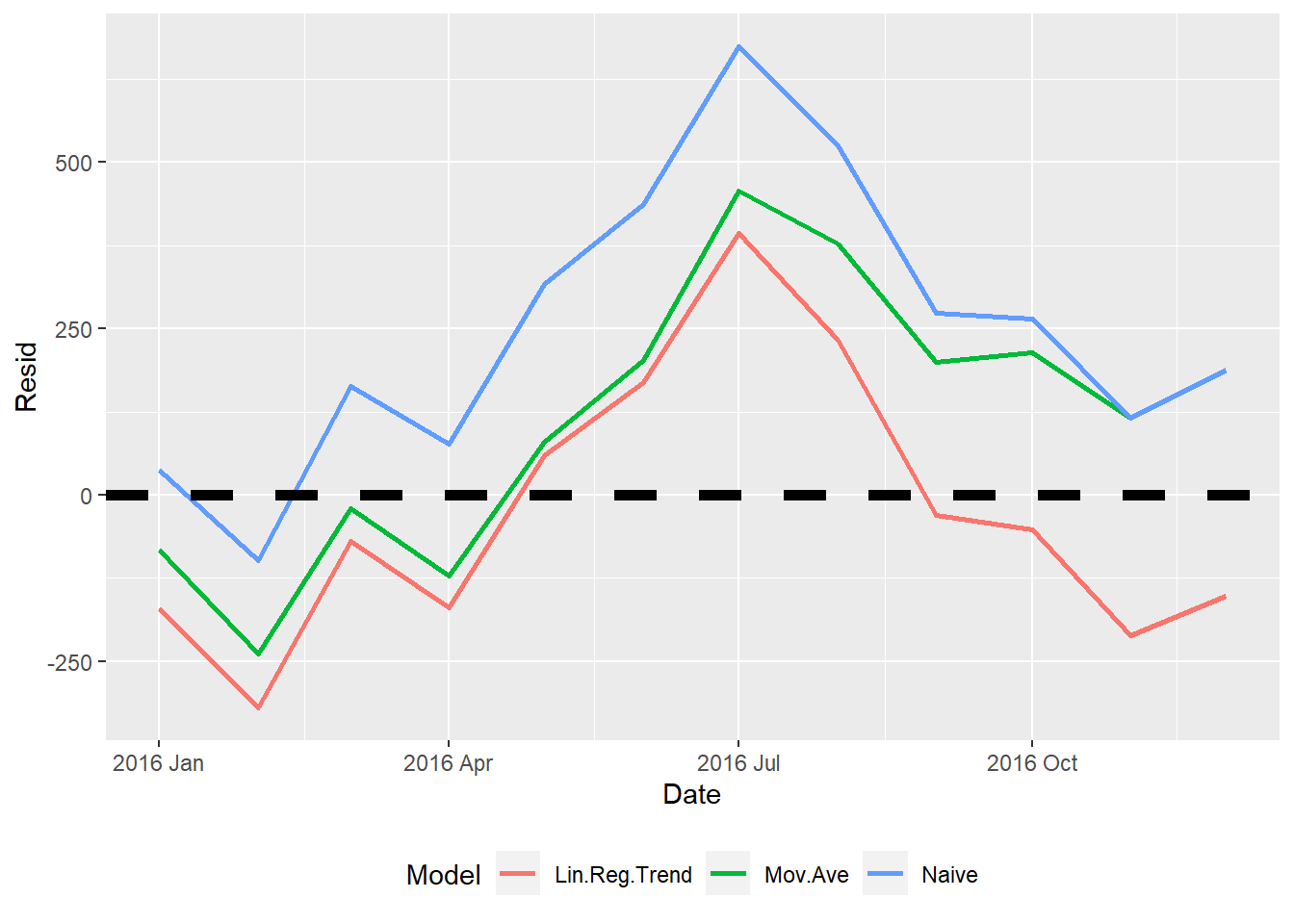
results <- list(naive, smooth, linreg)
models <- c("Naive", "Mov.Ave", "Lin.Reg.Trend")
fccompare(results, models)$acc
Model RMSE MAE MAPE
1 Naive 323.496 263.917 0.945
8 Mov.Ave 225.685 191.245 0.686
10 Lin.Reg.Trend 199.198 168.985 0.607
$fcresplot